Pigmentation
About Pigmentation
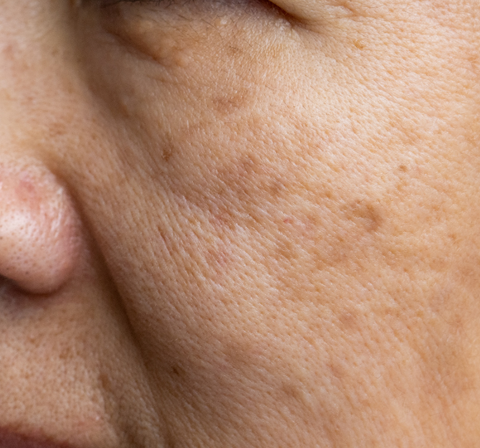
Pigmentation refers to the coloration of the skin, which is influenced by the amount and type of melanin produced by skin cells called melanocytes. Changes in pigmentation can manifest as dark spots, uneven skin tone, or discoloration. Here’s a detailed description
Types of Pigmentation Issues:
-
Hyperpigmentation: This is when certain areas of the skin become darker than the surrounding skin. Common forms include:
- Sunspots: Dark spots caused by prolonged sun exposure.
- Age Spots: Also known as liver spots, these occur with aging and sun exposure.
- Melasma: Dark patches, often on the face, typically triggered by hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or due to oral contraceptives.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin following an injury, inflammation, or acne.
-
Hypopigmentation: This occurs when the skin loses melanin, resulting in lighter patches. Common forms include:
- Vitiligo: A condition where patches of skin lose their pigment due to the destruction of melanocytes.
- Albinism: A genetic condition where the skin, hair, and eyes lack melanin entirely.
Causes of Pigmentation Changes:
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation stimulates melanin production, leading to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy or with the use of birth control, can trigger melasma.
- Inflammation or Injury: Skin trauma, acne, or dermatitis can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can predispose individuals to certain pigmentation disorders.
- Medications: Some medications can cause changes in skin pigmentation as a side effect.
Care Tips:
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen daily to prevent further darkening of existing pigmentation and protect against new spots.
- Topical Treatments: Products containing ingredients like vitamin C, hydroquinone, niacinamide, or retinoids can help lighten pigmentation and even out skin tone.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation can help remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of pigmentation.
- Consult a Dermatologist: For persistent or severe pigmentation issues, professional treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or prescription medications might be recommended.
Managing pigmentation often requires a combination of preventive measures and targeted treatments to achieve the best results.
Our Recommended Products
-
SKIN1004 Madagascar Centella Tone Brightening Cleansing Gel Foam 125ml
Regular price $26.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SKIN1004 Madagascar Centella Tone Brightening Booster Toner 210ml
Regular price $35.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SKIN1004 Madagascar Centella Tone Brightening Capsule Ampoule
Regular price From $30.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SKIN1004 Madagascar Centella Brightening Capsule Cream 75ml
Regular price $36.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
NUMBUZIN No.5 Vitamin Boosting Essence Toner 200ml
Regular price $38.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
NUMBUZIN No.5 Vitamin-Niacinamide Concentrated Pad 180ml x 70 Pads
Regular price $46.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
MEDICUBE - Deep Vita Capsule Cream 55g
Regular price $49.99 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
MIXSOON - Galactomyces Ferment Essence 100ml
Regular price $52.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
COSRX The Niacinamide 15 Serum 20ml
Regular price $41.95 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
COSRX Vita c23 Serum - 20ml
Regular price $41.99 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
ANUA Niacinamide 10% + TXA 4% Dark Spot Removing Serum 30ml
Regular price $44.95 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
BEAUTY OF JOSEON - Glow Serum; Propolis + Niacinamide
Regular price From $28.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
COMMONLAB Vitamin C Brightening Ampoule 30ml
Regular price $32.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
NEOGEN Dermalogy Real Vitamin C Serum 32g
Regular price $45.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
NUMBUZIN No.5 Vitamin Concentrated Serum 30ml
Regular price $46.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
 Sold out
Sold outANUA Green Lemon Vita C Serum 20ml
Regular price $54.95 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
TORRIDEN - CELLMAZING Brightening Mask 26ml x 1
Regular price $7.50 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
Mediheal Vitamide Brightening Pad 100 pads
Regular price $40.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
ANUA Peach Niacin Enriched Cream 50ml
Regular price $44.95 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SKIN1004 Madagascar Centella Tea Trica Soothing Sun Milk 50ml
Regular price $30.00 AUDRegular priceUnit price / per
Need help with something else?
-
-
-
Terms of Service
See our TermsUnderstand our terms and conditions for using our services and products.
Since 2016, Makeup2beauty has delivered authentic K-beauty products to Australia through direct partnerships with leading Korean brands, offering quality and competitive pricing.
...I am left amazed at the results I am able to achieve for my clients with Cellstory. It's a must have on our facial menu. I am always re-ordering this product! Results can be seen in as little as one treatment.
Blanc To Noir Maskbar Clients
...Cellstory eliminates the pain, bleeding, swelling and irritation often associated with microneedling. Cellstory helps minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles (specifically around the mouth, eyes, and forehead), acne, pigmentation, and uneven texture. "It gives an overall healthy, supple, [and] bouncy glow.
Dr. Engelman Maskbar Clients
...My skin looked, in the best way I can describe it, WOW. It was the cleanest and smoothest it has ever looked after a treatment. It was something beyond a miracle. In the hours following the treatment, the redness faded. The next morning, my skin looked healthy, glowy, and there wasn't a pore in sight.
Angela
...Loving my complexion after having received two treatments of the Miracle Tox with Co2 skin booster. Minimised pores and more glow! Staff are super nice too.
Milicia
...I went to get my first cellstory treatment and am already noticing that my skin is brighter and more nourished. The team at Maskbar are wonderful - they are professional and knowledgeable and you feel like you're in capable hands for an indulgent experience. I can't wait to come back for my next treatment!
Hayley Maskbar Clients
...I have been coming in for cell story treatment for skin scars and overall health and tone. My skin has improved significantly with the treatment sessions and products recommended pre- treatment skin analysis. Now can go out with no make up. Couldn't be happier with the quality of care and service provided by the therapist and their manners.
Sabah Dee
Makeup2beauty has consistently proven to be our most dependable supplier from the beginning. Their team is delightful to collaborate with and offer top notch support to our small business.
MASKBAR






















 Global Shipping
Global Shipping Same Day Delivery
Same Day Delivery Authenticity Guaranteed
Authenticity Guaranteed Money Back
Money Back



